DUAL TEST ( MATERNAL SERUM SCREEN – 2 )
“ Double test is a maternal blood screening test performed “ in the first trimester between 9-13 weeks of gestation. The specific substances analyzed are: Free Beta hCG, PAPP-A
Double test is a maternal blood screening test performed in the first trimester between 9-13 weeks of gestation. The specific substances analyzed are: Free Beta hCG, PAPP-A
FreeBeta HCG
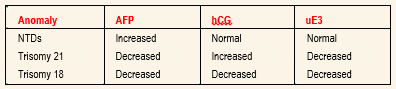
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a protein made by the placenta that consists of two subunits, alpha and beta. hCG is present in two forms: intact hCG (consisting of both alpha and beta subunits) and free Beta hCG (the beta subunit of hCG alone). Serum levels of hCG tend to be high in patients carrying a fetus affected with Down syndrome. The median concentration for free Beta hCG in the blood of women carrying fetuses with Down syndrome, measured as a multiple of the median (MoM), is 1.9 (compared to 1.0 for unaffected fetuses). This large difference provides the basis for the discrimination between affected and unaffected fetuses. Intact hCG, on the other hand, does not discriminate as well: its median MoM is less than 1.3. Furthermore, free Beta is significantly reduced in the blood of women carrying Trisomy 18 fetuses, with a median MoM of 0.18. Free Beta is the most specific and sensitive marker for Down syndrome and Trisomy 18.
The main advantage of measuring free Beta hCG, instead of intact hCG, is a significantly higher detection rate for a given false positive rate.
Pregnancy Associated Plasma Protein A (PAPP-A) is also produced by the placenta. PAPP-A is significantly reduced in the blood of women carrying fetuses with Down syndrome and Trisomy 18: the median MoMs are 0.44 and 0.32, respectively (compared to 1.0 for unaffected fetuses). These dramatic differences from normal provide excellent discrimination between affected and unaffected fetuses.
Nuchal Translucency
One of the single most important breakthroughs in chromosome abnormality screening was the ultrasonographic observation of a correlation between a nuchal translucency (accumulation of fluid at the back of the fetal neck) observed on ultrasound between 10 and 13 weeks and the incidence of Down syndrome and other abnormalities. NT is increased in fetuses with chromosome abnormalities, heart defects, and certain genetic syndromes.
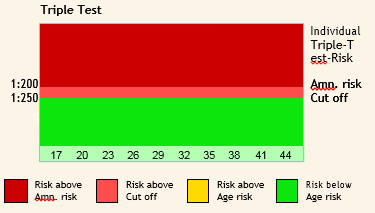
Combination of Double test with nuchal translucency increases the detection rate of both Trisomy 21 and 18. This test is performed between 11-13 weeks of gestation.