- Thyrocare_AN
- August 29, 2023
- Research
- 0 Comments

The liver is the largest organ inside one’s body, and it is responsible for many important bodily functions including:
- Storing vitamins, sugar, and iron to give the body energy.
- Controlling the production and removal of cholesterol.
- Clearing the blood of waste products, drugs, and other toxins.
- Releasing a substance called “bile” to help digest food and absorb nutrients.
However, when an infection occurs in the liver, it may cause damage to the liver cells, compromising its ability to function properly.
What Is Hepatitis B?
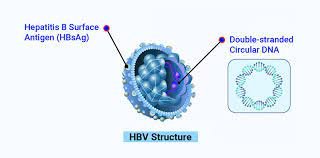
Hepatitis B, also called HBV or Hep B, is a type of viral infection that affects one’s liver. The word “hepatitis” is the medical term for “inflammation of the liver”, and it is one of the 5 types of hepatitis that can infect the liver, causing inflammation. Each type of infection – Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E, differs in terms of their symptoms, how they are transmitted, and their treatment.
Hepatitis B is one of the most common infections of the liver that affects children and adults. It is caused by the hepatitis B virus which attacks the liver cells, causing the liver to harden over time. Although common, if the symptoms of hepatitis B are detected early, only then can it be treated effectively.
Types of Hepatitis B
Depending on its duration and severity, there are two types of hepatitis B, namely, acute hepatitis B and chronic hepatitis B.
- Acute Hepatitis B
Acute Hepatitis B is short-term and the more common type of hepatitis. It usually resolves itself within 6 months, and mostly only occurs in adults. The symptoms of acute hepatitis B may range from mild to severe.
- Chronic Hepatitis B
Chronic Hepatitis B is a more severe form of the infection and may last for a lifetime. In most cases, it occurs in infants and children. This form of hepatitis may not display any symptoms in the early stages. However, it may lead to liver problems as one ages. While there is no cure for chronic hepatitis B, treatment goes a long way in helping manage the symptoms.
Symptoms of Hepatitis B
The signs and symptoms of hepatitis B may not be very prominent in the initial stages. In certain cases of acute hepatitis B, one may not have any symptoms at all.
If one does display hepatitis B symptoms, they may include:
Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
Dark urine
Fatigue or feeling very tired
Nausea and vomiting
Pain in the abdomen
Fever
Joint pain
Loss of appetite
Further, the hepatitis B symptoms in women are similar to the hepatitis B symptoms in men.
Causes and Transmission of Hepatitis B
The cause of hepatitis B is the hepatitis B virus, which can spread from person to person in a number of ways. Even if one is not experiencing any signs of HBV infection, it can still be transmitted to others.
The transmission of hep B virus may occur in the following ways:
Sexual intercourse
One of the primary reasons for contracting hepatitis B is having unprotected sexual intercourse with someone who has the virus in their body. The virus can enter the body through their partner’s saliva, semen, or vaginal secretions.
Sharing Needles
Another major cause of hepatitis B spreading is the sharing of needles or syringes contaminated with infected blood.
Pregnant Women
Pregnant women infected with HBV may also transmit the infection to their babies. This is a major reason for hepatitis B in children and infants.
Accidental Contact
Any accidental contact with infected blood can also cause hepatitis B.
It is important to note that the transmission of hep B does not happen through food, water, coughing and sneezing, or sharing utensils with an infected person
.
Dedicated Professionals & Doctors Recommend Us
Dedicated professionals committed to providing you with accurate and reliable diagnostic services. Get patholab services today from the best lab experts & make a visit to our laboratory.
Hepatitis B Diagnosis
Since the symptoms are more or less similar across different types of hepatitis, a blood test is required for the diagnosis of hepatitis B. Certain tests may also be prescribed to differentiate between acute and chronic hepatitis B. Physical examination, ultrasound, or a fibro scan may also be done to assess liver health and the severity of the infection. Timely diagnosis of hepatitis B helps in tailoring effective treatment plans.
Treatment for Hepatitis B
The treatment plan is different for acute and chronic hepatitis B.
For acute hepatitis B, the treatment plan is focused on making the person comfortable. They are advised to eat healthy foods and consume lots of water and fluids to keep themselves hydrated.
Treatment for chronic hepatitis B consists of oral medicines that help in:
Slowing down the progression of cirrhosis
Reducing the chances of liver cancer
Improving the quality of life
It is advisable to consult a healthcare practitioner at the first signs and symptoms of hepatitis B, so that appropriate steps may be taken.
Prevention of Hepatitis B
Although there is no cure for chronic hepatitis B, the hepatitis B vaccine is highly effective in preventing new infections. This vaccination is particularly important for infants born to infected mothers and for individuals at higher risk for the infection, due to various factors, like being in healthcare work, etc. Besides vaccination, practicing safe sex, avoiding sharing needles or personal items that may carry infected blood, and proper screening of blood products contribute to preventing the transmission of hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B is an infection that affects many people worldwide. A proper understanding of the signs and symptoms of HBV infection and a timely diagnosis can help one receive effective treatment and lead a healthy life.